1. Marketing is the process of Creating, Communicating and delivering Value to target market at a Profit.
2. Radical Marketing--> e.g. Boston Beer Company-->Instead of Spending heavily on advertising and big marketing budgets, company stretch the limited resources and stay close to competitors at grass root level and satisfy needs.
3. Customer Value= Functional+Emotional+Psychological
4. Marketing Channels:- The channels that are used to reach target market.
5.Integrated Marketing-> When all the departments of organization work together, to serve the cust
omer's interests and
6.Customer Equity:- Total discounted values of all the customers of firms
7.Customer Development Process----> Suspects---> Prospects---> First time Customers---> Repeat time customers-->Clients---> Members--> Advocates-->Partners
Strategic Marketing Plan
Here Y axis is a % scale and X- axis is a logarithm scale
Research Instruments
1. Questionnaire
2. Psychological tools---> Laddering techniques, Indepth Interviews,
3. Mechanical Devices----> POS data and galvano meters used to measure emotions
Forecasting Process
1. Macroeconomic forecast projects
2. Industry Forecast
3. Company Forecast
Methods of forecasts:-
1. Survey of Buyer's intentions
2. Composite of Sales force opinion
3. Expert Opinion
4. Post Sales Analysis
5. Market test method
Technology Adoption Cycle
Product Life Cycle
![]()
Services Marketing
Services Marketing involves 7P's ----> 4P's + People+ Physical Evidence+ Process
Three types of marketing of services:-
![]()
Pricing
Pricing involves six steps:-
1. Select the pricing objective:- Survival, Max Profits, Max Market Share, Market Skimming or Product Quality Leadership...
2. Determining Demand:- Each price will have different demand.Demand curves can be estimated in three ways:-
3. Estimating Costs:- Fixed Costs + Variable costs = Total Cost
Average Cost = (Total Cost)/ Production Units
Experience or Learning Curve
The experience curve effect is broader in scope than the learning curve effect encompassing far more than just labor time. It states that the more often a task is performed, the lower will be the cost of doing it. The task can be the production of any good or service. Each time cumulative volume doubles, value added costs (including administration, marketing, distribution, and manufacturing) fall by a constant and predictable percentage.
Costing Methods
There are two methods of costing:-
1. ABC Costing
2. Target Costing
ABC Costing:- It is used to link costs to each activity and costing is done according to each activity
Target Costing:- Here company fixed the desired profitability and accordingly decide the price.
Seven Pricing Techniques
a. Mark up Pricing--> Add a standard markup to production cost.
b. Target Return Pricing-> Determine the price based on return of investment
c.Perceived Value Pricing-> Based on consumer's perceived value and the key is to deliver more value than competitors that to customers
d. Value Pricing--> Charging a fairly low price for high quality offering.
e. Going rate Pricing:- Firm based its pricing majorly on the competitor pricing and it is common for commodities such as steel and paper.
f. Auction- Type Pricing--> Getting popular on the internet such as ebay. Types of Auctioning:-
---> English Auctions and Sealed Bid Auctions( Popular for Govt auctions)
Group Pricing:-
Companies must ask this vital question---> How can we reach to our customers and how can they reach us?
Strategy is only differentiation and the things you do better to control of your resources
Loading............
For more check this out!! www.ashish-badyal.com
2. Radical Marketing--> e.g. Boston Beer Company-->Instead of Spending heavily on advertising and big marketing budgets, company stretch the limited resources and stay close to competitors at grass root level and satisfy needs.
3. Customer Value= Functional+Emotional+Psychological
4. Marketing Channels:- The channels that are used to reach target market.
5.Integrated Marketing-> When all the departments of organization work together, to serve the cust
omer's interests and
6.Customer Equity:- Total discounted values of all the customers of firms
7.Customer Development Process----> Suspects---> Prospects---> First time Customers---> Repeat time customers-->Clients---> Members--> Advocates-->Partners
Strategic Marketing Plan
Product portfolio - the Boston Matrix (or Boston Box)
The business portfolio is the collection of businesses
and products that make up the company. The best business portfolio is one
that fits the company's strengths and helps exploit the most attractive opportunities.( By attractive opportunities, we mean markets where growth is high and size of entire market is increasing)
The company must:
(1) Analyse its current business portfolio and decide which
businesses should receive more or less investment, and
(2) Develop growth strategies for adding new products and businesses
to the portfolio, whilst at the same time deciding when products and businesses
should no longer be retained.
Methods of Portfolio Planning
The two best-known portfolio planning methods are from the Boston
Consulting Group and by General Electric/Shell.
In each method, the first step is to identify the various Strategic Business
Units ("SBU's") in a company portfolio. An SBU is a unit of the
company that has a separate mission and objectives and that can be planned
independently from the other businesses. An SBU can be a company division,
a product line or even individual brands - it all depends on how the company
is organised.
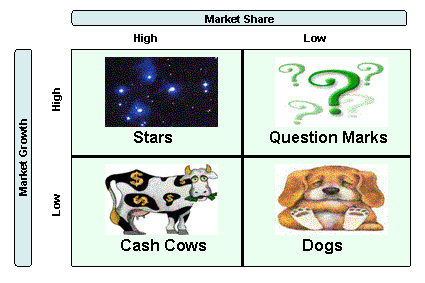
The Boston Consulting Group Box ("BCG Box")

Here Y axis is a % scale and X- axis is a logarithm scale
Using the BCG Box (an example is illustrated above) a company
classifies all its SBU's according to two dimensions:
On the horizontal axis: relative market share -
this serves as a measure of SBU strength in the market
On the vertical axis: market growth rate - this
provides a measure of market attractiveness
By dividing the matrix into four areas, four types of SBU can
be distinguished:
Stars - Stars are high growth businesses or products
competing in markets where they are relatively strong compared with the competition.
Often they need heavy investment to sustain their growth. Eventually their
growth will slow and, assuming they maintain their relative market share,
will become cash cows.
Cash Cows - Cash cows are low-growth businesses or products
with a relatively high market share. These are mature, successful businesses
with relatively little need for investment. They need to be managed for continued
profit - so that they continue to generate the strong cash flows that the
company needs for its Stars.
Question marks - Question marks are businesses or products
with low market share but which operate in higher growth markets. This suggests
that they have potential, but may require substantial investment in order
to grow market share at the expense of more powerful competitors. Management
have to think hard about "question marks" - which ones should they
invest in? Which ones should they allow to fail or shrink?
Dogs - Unsurprisingly, the term "dogs" refers
to businesses or products that have low relative share in unattractive, low-growth
markets. Dogs may generate enough cash to break-even, but they are rarely,
if ever, worth investing in.
Using the BCG Box to determine strategy
Once a company has classified its SBU's, it must decide what
to do with them. In the diagram above, the company has one large cash cow
(the size of the circle is proportional to the SBU's sales), a large dog and
two, smaller stars and question marks.
Conventional strategic thinking suggests there are four possible
strategies for each SBU:
(1) Build Share: here the company can invest to
increase market share (for example turning a "question mark" into
a star)
(2) Hold: here the company invests just enough
to keep the SBU in its present position
(3) Harvest: here the company reduces the amount
of investment in order to maximise the short-term cash flows and profits from
the SBU. This may have the effect of turning Stars into Cash Cows.
(4) Divest: the company can divest the SBU by
phasing it out or selling it - in order to use the resources elsewhere (e.g.
investing in the more promising "question marks").
Another model on Business Portfolio Evaluation is GE Shell Matrix which works on the industry attractiveness and
Three ways to grow business:-
1. Intensive Growth
2. Integrative Growth
3. Diversification Growth
Intensive Growth Strategies
Market Penetration Strategies include Competition Pricing, Advertising, Promotions,Increasing Sales Team, Increasing Usage using Loyalty schemes.
Market Development Strategies include new geographical markets, new differentiation, new distribution channels and different pricing policy.
Integrative Growth Strategies
Backward Integration---> Acquiring a Supplier
Forward Integration---> Acquiring a Distributor
Horizontal Integration---->Acquiring a Competitor
Diversification Growth Strategies
There are three diversification Strategies:-
1. Concentric Diversification---> Products that have tech and other specifications to the exiting products.
2. Horizontal Diversification------> Products that will appeal to the current customer but the products are unrelated to the current product line
3. Conglomerate Diversification:- Unrelated markets and unrelated products
2. Horizontal Diversification------> Products that will appeal to the current customer but the products are unrelated to the current product line
3. Conglomerate Diversification:- Unrelated markets and unrelated products
Marketing Plan
1. Executive Summary
2. Market Overview+
2. Market Overview+
3. Market Analysis---> Industry Analysis, Macroeconomic Factors
4. Oppurtunity Analysis
5. Firm Analysis---> SWOT
6. Objectives---> Major marketing and financial objectives
7. Marketing Strategy--> STP, Marketing Mix
8. Financial Projections
9.Controls--> Marketing Audit
Marketing Research Process
1. Define the problem and research objectives
2. Develop the research methodology
3.Collection of information
4.Analyze the information
5. Present the findings
4. Oppurtunity Analysis
5. Firm Analysis---> SWOT
6. Objectives---> Major marketing and financial objectives
7. Marketing Strategy--> STP, Marketing Mix
8. Financial Projections
9.Controls--> Marketing Audit
Marketing Research Process
1. Define the problem and research objectives
2. Develop the research methodology
3.Collection of information
4.Analyze the information
5. Present the findings
Types of researches
1. Exploratory:- ~To shed light on the nature of problem ----> what and when?
2. Descriptive & Diagnostic:- To ascertain certain magnitudes----> Why?
3. Causal---> To test cause and effect
Primary Data Collection Approaches
1. Observational Research
2. Focus Groups
3. Survey
1. Exploratory:- ~To shed light on the nature of problem ----> what and when?
2. Descriptive & Diagnostic:- To ascertain certain magnitudes----> Why?
3. Causal---> To test cause and effect
Primary Data Collection Approaches
1. Observational Research
2. Focus Groups
3. Survey
4.Behavioral
5.Experimental
Research Instruments
1. Questionnaire
2. Psychological tools---> Laddering techniques, Indepth Interviews,
3. Mechanical Devices----> POS data and galvano meters used to measure emotions
Forecasting Process
1. Macroeconomic forecast projects
2. Industry Forecast
3. Company Forecast
Methods of forecasts:-
1. Survey of Buyer's intentions
2. Composite of Sales force opinion
3. Expert Opinion
4. Post Sales Analysis
5. Market test method
Technology Adoption Cycle
Product Life Cycle
Services Marketing
Services Marketing involves 7P's ----> 4P's + People+ Physical Evidence+ Process
Three types of marketing of services:-
Pricing
Pricing involves six steps:-
1. Select the pricing objective:- Survival, Max Profits, Max Market Share, Market Skimming or Product Quality Leadership...
2. Determining Demand:- Each price will have different demand.Demand curves can be estimated in three ways:-
3. Estimating Costs:- Fixed Costs + Variable costs = Total Cost
Average Cost = (Total Cost)/ Production Units
Experience or Learning Curve
The experience curve effect is broader in scope than the learning curve effect encompassing far more than just labor time. It states that the more often a task is performed, the lower will be the cost of doing it. The task can be the production of any good or service. Each time cumulative volume doubles, value added costs (including administration, marketing, distribution, and manufacturing) fall by a constant and predictable percentage.
Costing Methods
There are two methods of costing:-
1. ABC Costing
2. Target Costing
ABC Costing:- It is used to link costs to each activity and costing is done according to each activity
Target Costing:- Here company fixed the desired profitability and accordingly decide the price.
Seven Pricing Techniques
a. Mark up Pricing--> Add a standard markup to production cost.
b. Target Return Pricing-> Determine the price based on return of investment
c.Perceived Value Pricing-> Based on consumer's perceived value and the key is to deliver more value than competitors that to customers
d. Value Pricing--> Charging a fairly low price for high quality offering.
e. Going rate Pricing:- Firm based its pricing majorly on the competitor pricing and it is common for commodities such as steel and paper.
f. Auction- Type Pricing--> Getting popular on the internet such as ebay. Types of Auctioning:-
---> English Auctions and Sealed Bid Auctions( Popular for Govt auctions)
Group Pricing:-
Companies must ask this vital question---> How can we reach to our customers and how can they reach us?
Strategy is only differentiation and the things you do better to control of your resources
Loading............
For more check this out!! www.ashish-badyal.com
